Potomac River on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Potomac River () drains the Mid-Atlantic
The National Map
. Retrieved August 15, 2011 with a
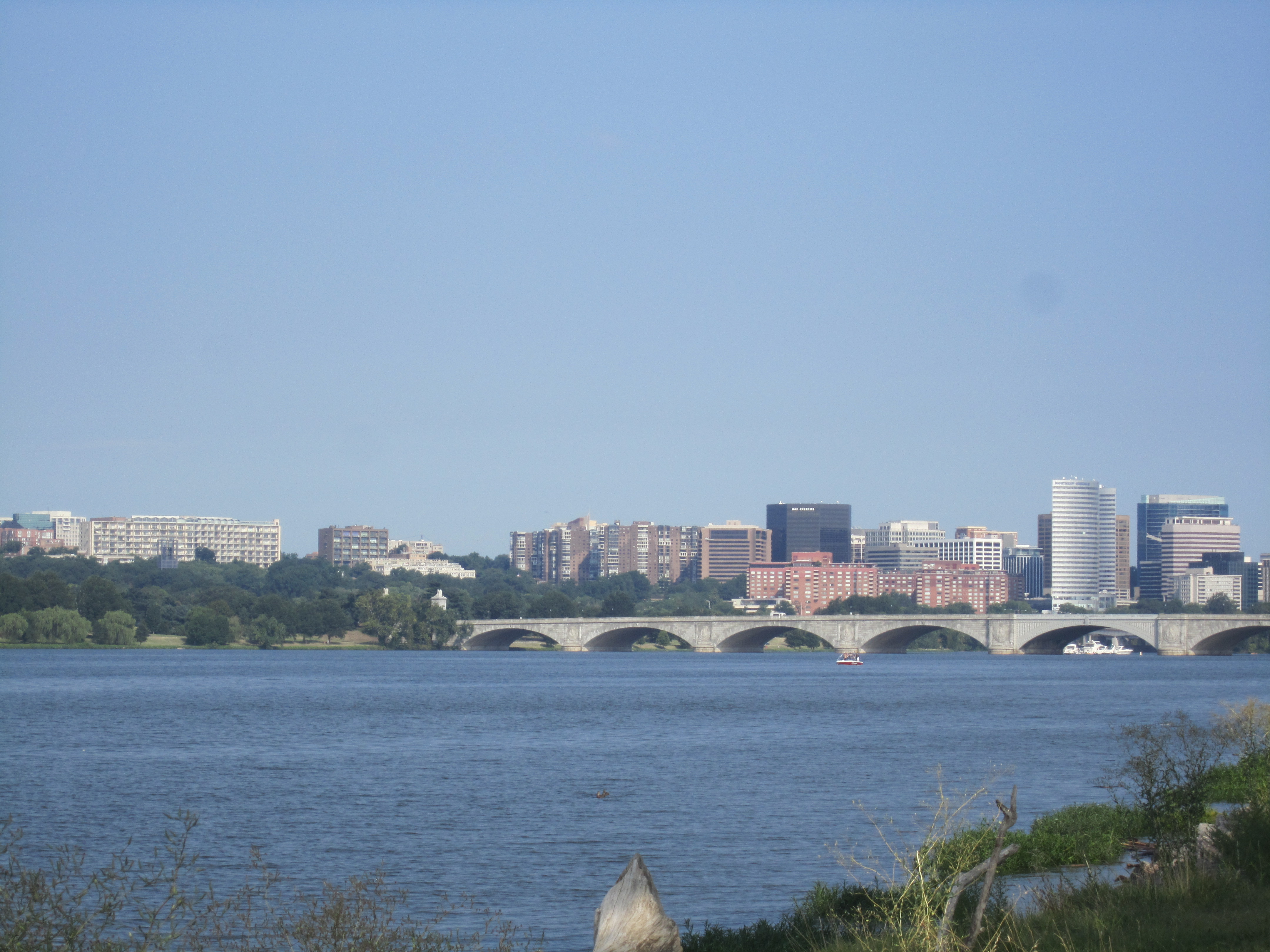 The Potomac River runs from
The Potomac River runs from  The river has two sources. The source of the North Branch is at the Fairfax Stone located at the junction of
The river has two sources. The source of the North Branch is at the Fairfax Stone located at the junction of
 The source of the North Branch Potomac River is at the
The source of the North Branch Potomac River is at the
 In its eastern course from Petersburg into Hardy County, the South Branch becomes more navigable allowing for
In its eastern course from Petersburg into Hardy County, the South Branch becomes more navigable allowing for
 This section covers the Potomac from just above Harpers Ferry in West Virginia down to Little Falls, Maryland on the border between Maryland and Washington, DC. Along the way the following tributaries drain into the Potomac:
This section covers the Potomac from just above Harpers Ferry in West Virginia down to Little Falls, Maryland on the border between Maryland and Washington, DC. Along the way the following tributaries drain into the Potomac:
 "Potomac" is a European spelling of ''
"Potomac" is a European spelling of '' The similarity of the name to the Ancient Greek word for river, ''potamos'', has been noted for more than two centuries but it appears to be due to chance.
The Potomac River brings together a variety of cultures throughout the watershed from the coal miners of upstream West Virginia to the urban residents of the nation's capital and, along the lower Potomac, the watermen of Virginia's Northern Neck.
The similarity of the name to the Ancient Greek word for river, ''potamos'', has been noted for more than two centuries but it appears to be due to chance.
The Potomac River brings together a variety of cultures throughout the watershed from the coal miners of upstream West Virginia to the urban residents of the nation's capital and, along the lower Potomac, the watermen of Virginia's Northern Neck.

 Being situated in an area rich in
Being situated in an area rich in  General Robert E. Lee crossed the river, thereby invading the North and threatening Washington, D.C., twice in campaigns climaxing in the battles of
General Robert E. Lee crossed the river, thereby invading the North and threatening Washington, D.C., twice in campaigns climaxing in the battles of
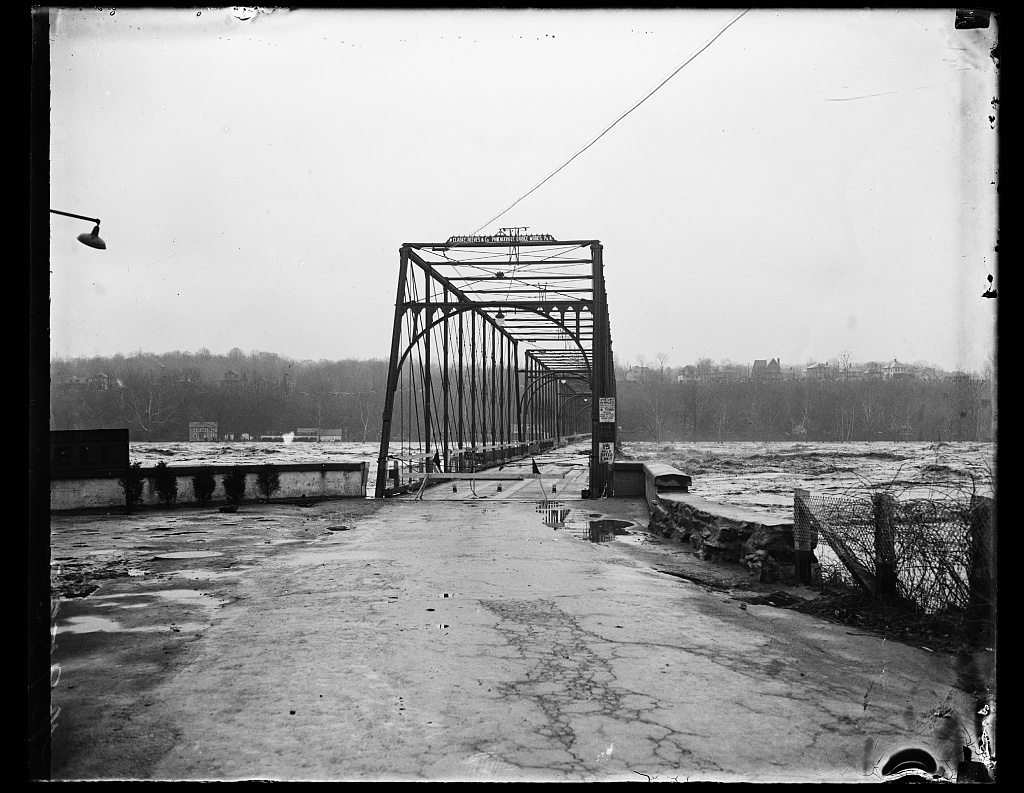 As a result of damaging floods in 1936 and 1937, the Army Corps of Engineers proposed the
As a result of damaging floods in 1936 and 1937, the Army Corps of Engineers proposed the
"Capital Engineers: The U.S. Army Corps of Engineers in the Development of Washington, D.C., 1790–2004."
(Washington, DC: U.S. Army Corps of Engineers.) Publication No. EP 870-1-67. p. 256. In 1940
"Potomac Timeline."
Updated 2008-04-15. Beginning in the 19th century, with increasing
Beginning in the 19th century, with increasing
 The average daily flow during the
The average daily flow during the
 The original charters are silent as to which branch from the upper Potomac serves as the boundary, but this was settled by the 1785 Compact. When West Virginia
The original charters are silent as to which branch from the upper Potomac serves as the boundary, but this was settled by the 1785 Compact. When West Virginia
 A variety of fish inhabit the Potomac, including bass,
A variety of fish inhabit the Potomac, including bass,
 Early European colonists who settled along the Potomac found a diversity of large and small mammals living in the dense forests nearby. Bison,
Early European colonists who settled along the Potomac found a diversity of large and small mammals living in the dense forests nearby. Bison,
Potomac-Chesapeake Dolphin Project
more than 500 individual members of the species have been identified in the Potomac during this period.










Advanced Hydrologic Prediction Service
Baltimore/Washington (Sterling, VA)
- including Potomac River levels ** Potomac River level a
Williamsport
** Potomac River level a
Harpers Ferry
** Potomac River level a
Point of Rocks
** Potomac River level a
Little Falls
** Potomac River level a
Wisconsin Avenue
''Geology of the National Capital Region: Field Trip Guidebook'' (2004) edited by Scott Southworth, William Chapin Burton, Reston, VA: U.S. Geological Survey
''Guide to Spring Wildflowers on the Towpath'' (2010) compiled by the C&O Canal Association Nature Committee
Interstate Commission on the Potomac River Basin (ICPRB)
Potomac Conservancy
Potomac Heritage National Scenic Trail
Potomac Riverkeeper
Potomac Timeline
(focus on water quality) by ICPRB
Potomac Watershed Partnership
Potomac Watershed Roundtable
Prince William Conservation Alliance
Stewards of the Potomac Highlands
South Branch Consortium
also available in ttps://pubs.usgs.gov/bul/1471/report.pdf downloadable pdf format* [https://pubs.usgs.gov/of/1997/0060/report.pdf ''The Seven-Storey River: Geomorphology of the Potomac River Channel Between Blockhouse Point, Maryland, and Georgetown, District of Columbia, With Emphasis on the Gorge Complex Below Great Falls'' (1997) by E-an Zen, Reston, VA: US Geological Survey]
VEGETATION ECOLOGY OF THE POTOMAC GORGE
by the Virginia Department of Conservation and Recreation, Division of Natural Heritage
West Virginia Division of Natural Resources
West Virginia Rivers Coalition
* ttp://www.switchfisher.com/admin/CatchGuides/CG-UPCatchguide.html Wade and Shoreline Fishing the Potomac River for Smallmouth Bass {{Authority control Rivers of Washington, D.C. Rivers of Maryland Rivers of Virginia Rivers of West Virginia Monongahela National Forest History of West Virginia Borders of Maryland Borders of Virginia Borders of West Virginia American Heritage Rivers Tributaries of the Chesapeake Bay
United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territorie ...
, flowing from the Potomac Highlands
The Potomac Highlands of West Virginia (or just the Potomac Highlands) () centers on five West Virginian counties (Grant, Hampshire, Hardy, Mineral, and Pendleton) in the upper Potomac River watershed in the western portion of the state's Eastern ...
into Chesapeake Bay
The Chesapeake Bay ( ) is the largest estuary in the United States. The Bay is located in the Mid-Atlantic region and is primarily separated from the Atlantic Ocean by the Delmarva Peninsula (including the parts: the Eastern Shore of Maryland / ...
. It is long,U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map
. Retrieved August 15, 2011 with a
drainage area
A drainage basin is an area of land where all flowing surface water converges to a single point, such as a river mouth, or flows into another body of water, such as a lake or ocean. A basin is separated from adjacent basins by a perimeter, t ...
of 14,700 square miles (38,000 km2), and is the fourth-largest river along the East Coast of the United States and the 21st-largest in the United States. Over 5 million people live within its watershed.
The river forms part of the borders between Maryland
Maryland ( ) is a state in the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States. It shares borders with Virginia, West Virginia, and the District of Columbia to its south and west; Pennsylvania to its north; and Delaware and the Atlantic Ocean to ...
and Washington, D.C.
)
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = Clockwise from top left: the Washington Monument and Lincoln Memorial on the National Mall, United States Capitol, Logan Circle, Jefferson Memorial, White House, Adams Morgan, ...
on the left descending bank and between West Virginia
West Virginia is a state in the Appalachian, Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States.The Census Bureau and the Association of American Geographers classify West Virginia as part of the Southern United States while the B ...
and Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States, between the Atlantic Coast and the Appalachian Mountains. The geography and climate of the Commonwealth ar ...
on the right descending bank. Except for a small portion of its headwaters in West Virginia, the North Branch Potomac River
The North Branch Potomac River flows from Fairfax Stone in West Virginia to its confluence with the South Branch Potomac River near Green Spring, West Virginia, where it turns into the Potomac River proper.
Course
From the Fairfax Stone, th ...
is considered part of Maryland to the low-water mark on the opposite bank. The South Branch Potomac River
The South Branch Potomac River has its headwaters in northwestern Highland County, Virginia near Hightown along the eastern edge of the Allegheny Front. After a river distance of ,U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolu ...
lies completely within the state of West Virginia except for its headwaters
The headwaters of a river or stream is the farthest place in that river or stream from its estuary or downstream confluence with another river, as measured along the course of the river. It is also known as a river's source.
Definition
The ...
, which lie in Virginia.
Course
Fairfax Stone Historical Monument State Park
Fairfax Stone Historical Monument State Park is a West Virginia state park commemorating the Fairfax Stone, a surveyor's marker and boundary stone at the source of the North Branch of the Potomac River. The original stone was placed on October ...
in West Virginia on the Allegheny Plateau
The Allegheny Plateau , in the United States, is a large dissected plateau area of the Appalachian Mountains in western and central New York (state), New York, northern and western Pennsylvania, northern and western West Virginia, and eastern Oh ...
to Point Lookout, Maryland, and drains . The length of the river from the junction of its North and South Branches to Point Lookout is .
 The river has two sources. The source of the North Branch is at the Fairfax Stone located at the junction of
The river has two sources. The source of the North Branch is at the Fairfax Stone located at the junction of Grant
Grant or Grants may refer to:
Places
*Grant County (disambiguation)
Australia
* Grant, Queensland, a locality in the Barcaldine Region, Queensland, Australia
United Kingdom
* Castle Grant
United States
* Grant, Alabama
* Grant, Inyo County, ...
, Tucker
Tucker may refer to:
Places United States
* Tucker, Arkansas
* Tucker, Georgia
* Tucker, Mississippi
* Tucker, Missouri
* Tucker, Utah, ghost town
* Tucker County, West Virginia
Outer space
* Tucker (crater), a small lunar impact crater in the s ...
, and Preston counties in West Virginia
West Virginia is a state in the Appalachian, Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States.The Census Bureau and the Association of American Geographers classify West Virginia as part of the Southern United States while the B ...
. The source of the South Branch is located near Hightown in northern Highland County, Virginia. The river's two branches converge just east of Green Spring in Hampshire County, West Virginia, to form the Potomac. As it flows from its headwaters
The headwaters of a river or stream is the farthest place in that river or stream from its estuary or downstream confluence with another river, as measured along the course of the river. It is also known as a river's source.
Definition
The ...
down to the Chesapeake Bay, the Potomac traverses five geological provinces: the Appalachian Plateau
The Appalachian Plateau is a series of rugged dissected plateaus located on the western side of the Appalachian Mountains. The Appalachian Mountains are a mountain range that run down the Eastern United States.
The Appalachian Plateau is the nor ...
, the Ridge and Valley
The Ridge-and-Valley Appalachians, also called the Ridge and Valley Province or the Valley and Ridge Appalachians, are a physiographic province of the larger Appalachian division and are also a belt within the Appalachian Mountains extending ...
, the Blue Ridge, the Piedmont Plateau
The Piedmont is a plateau region located in the Eastern United States. It is situated between the Atlantic coastal plain and the main Appalachian Mountains, stretching from New York in the north to central Alabama in the south. The Piedmont ...
, and the Atlantic coastal plain.
Once the Potomac drops from the Piedmont
it, Piemontese
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 =
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographics1_title1 =
, demographics1_info1 =
, demographics1_title2 ...
to the Coastal Plain
A coastal plain is flat, low-lying land adjacent to a sea coast. A fall line commonly marks the border between a coastal plain and a piedmont area. Some of the largest coastal plains are in Alaska and the southeastern United States. The Gulf Coa ...
at the Atlantic Seaboard fall line at Little Falls, tides further influence the river as it passes through Washington, D.C. and beyond. Salinity in the Potomac River Estuary increases thereafter with distance downstream. The estuary
An estuary is a partially enclosed coastal body of brackish water with one or more rivers or streams flowing into it, and with a free connection to the open sea. Estuaries form a transition zone between river environments and maritime environment ...
also widens, reaching 11 statute miles (17 km) wide at its mouth, between Point Lookout, Maryland, and Smith Point, Virginia, before flowing into the Chesapeake Bay.
North Branch Potomac River
 The source of the North Branch Potomac River is at the
The source of the North Branch Potomac River is at the Fairfax Stone
Fairfax Stone Historical Monument State Park is a West Virginia state park commemorating the Fairfax Stone, a surveyor's marker and boundary stone at the source of the North Branch of the Potomac River. The original stone was placed on Octobe ...
located at the junction of Grant
Grant or Grants may refer to:
Places
*Grant County (disambiguation)
Australia
* Grant, Queensland, a locality in the Barcaldine Region, Queensland, Australia
United Kingdom
* Castle Grant
United States
* Grant, Alabama
* Grant, Inyo County, ...
, Tucker
Tucker may refer to:
Places United States
* Tucker, Arkansas
* Tucker, Georgia
* Tucker, Mississippi
* Tucker, Missouri
* Tucker, Utah, ghost town
* Tucker County, West Virginia
Outer space
* Tucker (crater), a small lunar impact crater in the s ...
and Preston counties in West Virginia. From the Fairfax Stone, the North Branch Potomac River flows to the man-made Jennings Randolph Lake
Jennings Randolph Lake is a reservoir of located on the North Branch Potomac River in Garrett County, Maryland and Mineral County, West Virginia. It is approximately eight miles upstream of Bloomington, Maryland, and approximately five miles n ...
, an impoundment designed for flood control and emergency water supply. Below the dam, the North Branch cuts a serpentine path through the eastern Allegheny Mountains. First, it flows northeast by the communities of Bloomington, Luke
People
*Luke (given name), a masculine given name (including a list of people and characters with the name)
*Luke (surname) (including a list of people and characters with the name)
*Luke the Evangelist, author of the Gospel of Luke. Also known as ...
, and Westernport in Maryland and then on by Keyser, West Virginia to Cumberland, Maryland. At Cumberland, the river turns southeast. downstream from its source, the North Branch is joined by the South Branch between Green Spring and South Branch Depot, West Virginia from whence it flows past Hancock Hancock may refer to:
Places in the United States
* Hancock, Iowa
* Hancock, Maine
* Hancock, Maryland
* Hancock, Massachusetts
* Hancock, Michigan
* Hancock, Minnesota
* Hancock, Missouri
* Hancock, New Hampshire
** Hancock (CDP), New Hampshir ...
, Maryland and turns southeast once more on its way toward Washington, D.C.
)
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = Clockwise from top left: the Washington Monument and Lincoln Memorial on the National Mall, United States Capitol, Logan Circle, Jefferson Memorial, White House, Adams Morgan, ...
, and the Chesapeake Bay
The Chesapeake Bay ( ) is the largest estuary in the United States. The Bay is located in the Mid-Atlantic region and is primarily separated from the Atlantic Ocean by the Delmarva Peninsula (including the parts: the Eastern Shore of Maryland / ...
.
South Branch Potomac River
The exact location of the South Branch's source is northwest of Hightown along U.S. Route 250 on the eastern side of Lantz Mountain (3,934 ft) in Highland County. From Hightown, the South Branch is a small meandering stream that flows northeast along Blue Grass Valley Road through the communities of New Hampden and Blue Grass. At Forks of Waters, the South Branch joins with Strait Creek and flows north across the Virginia/West Virginia border into Pendleton County. The river then travels on a northeastern course along the western side of Jack Mountain (4,045 ft), followed by Sandy Ridge (2,297 ft) alongU.S. Route 220
U.S. Route 220 (US 220) is a spur route of US 20. It runs in a north–south layout in the eastern United States, unlike its parent route as well as conventionally even-numbered highways which run east-west. US 220 extends for f ...
. North of the confluence of the South Branch with Smith Creek, the river flows along Town Mountain (2,848 ft) around Franklin
Franklin may refer to:
People
* Franklin (given name)
* Franklin (surname)
* Franklin (class), a member of a historical English social class
Places Australia
* Franklin, Tasmania, a township
* Division of Franklin, federal electoral d ...
at the junction of U.S. Route 220 and U.S. Route 33
U.S. Route 33 (US 33) is a United States Numbered Highway that runs northwest–southeast for from northern Indiana to Richmond, Virginia, passing through Ohio and West Virginia en route. Although most odd-numbered U.S. routes are north– ...
. After Franklin, the South Branch continues north through the Monongahela National Forest
The Monongahela National Forest is a national forest located in the Allegheny Mountains of eastern West Virginia, USA. It protects over of federally managed land within a proclamation boundary that includes much of the Potomac Highlands Regi ...
to Upper Tract where it joins with three sizeable streams: Reeds Creek, Mill Run, and Deer Run.
Between Big Mountain (2,582 ft) and Cave Mountain (2,821 ft), the South Branch bends around the Eagle Rock (1,483 ft) outcrop and continues its flow northward into Grant County Grant County may refer to:
Places
;Australia
* County of Grant, Victoria
;United States
*Grant County, Arkansas
*Grant County, Indiana
* Grant County, Kansas
*Grant County, Kentucky
*Grant County, Minnesota
*Grant County, Nebraska
*Grant C ...
. Into Grant, the South Branch follows the western side of Cave Mountain through the long Smoke Hole Canyon
Smoke Hole Canyon — traditionally called The Smoke Holes and later simply Smoke Hole — is a rugged long gorge carved by the South Branch Potomac River in the Allegheny Mountains of eastern West Virginia, United States. The area is rather iso ...
, until its confluence with the North Fork at Cabins, where it flows east to Petersburg. At Petersburg, the South Branch Valley Railroad
The South Branch Valley Railroad is a railroad in the Eastern Panhandle of West Virginia. The branch line, which parallels the South Branch Potomac River, runs north from Petersburg to Green Spring, where it connects to the national rail net ...
begins, which parallelsthe river until its mouth at Green Spring.
 In its eastern course from Petersburg into Hardy County, the South Branch becomes more navigable allowing for
In its eastern course from Petersburg into Hardy County, the South Branch becomes more navigable allowing for canoes
A canoe is a lightweight narrow water vessel, typically pointed at both ends and open on top, propelled by one or more seated or kneeling paddlers facing the direction of travel and using a single-bladed paddle.
In British English, the ter ...
and smaller river vessels. The river splits and forms a series of large islands while it heads northeast to Moorefield. At Moorefield, the South Branch is joined by the South Fork South Branch Potomac River and runs north to Old Fields where it is fed by Anderson Run and Stony Run.
At McNeill
McNeill may refer to:
* McNeill (surname)
* McNeill, Mississippi, United States; an unincorporated community
* McNeill, West Virginia, United States; an unincorporated community
* Port McNeill, British Columbia, Canada; a town
* McNeill Bay ( ...
, the South Branch flows into the Trough
The Trough is a 6-mile long wooded gorge carved by the South Branch Potomac River (SBPR) and situated in the Allegheny Mountains of Hampshire and Hardy Counties, West Virginia, USA. The area was the site of a 1756 skirmish of the French and In ...
where it is bound to its west by Mill Creek Mountain
Mill Creek Mountain is a continuous mountain ridge that runs northeast through Hampshire and Hardy counties in the Eastern Panhandle region of the U.S. state of West Virginia. Rising to its greatest elevation of at High Knob, Mill Creek is a fo ...
(2,119 ft) and to its east by Sawmill Ridge (1,644 ft). This area is the habitat to bald eagles. The Trough passes into Hampshire County and ends at its confluence with Sawmill Run south of Glebe
Glebe (; also known as church furlong, rectory manor or parson's close(s))McGurk 1970, p. 17 is an area of land within an ecclesiastical parish used to support a parish priest. The land may be owned by the church, or its profits may be reserved ...
and Sector
Sector may refer to:
Places
* Sector, West Virginia, U.S.
Geometry
* Circular sector, the portion of a disc enclosed by two radii and a circular arc
* Hyperbolic sector, a region enclosed by two radii and a hyperbolic arc
* Spherical sector, a p ...
.
The South Branch continues north parallel to South Branch River Road
South is one of the cardinal directions or compass points. The direction is the opposite of north and is perpendicular to both east and west.
Etymology
The word ''south'' comes from Old English ''sūþ'', from earlier Proto-Germanic ''*sunþaz ...
( County Route 8) toward Romney with a number of historic plantation farms adjoining it. En route to Romney, the river is fed by Buffalo Run, Mill Run, McDowell Run, and Mill Creek at Vanderlip. The South Branch is traversed by the Northwestern Turnpike
The Northwestern Turnpike is a historic road in West Virginia (Virginia at the time the road was created), important for being historically one of the major roads crossing the Appalachians, financed by the Virginia Board of Public Works in the 183 ...
(U.S. Route 50
U.S. Route 50 or U.S. Highway 50 (US 50) is a major east–west route of the U.S. Highway system, stretching from Interstate 80 (I-80) in West Sacramento, California, to Maryland Route 528 (MD 528) in Ocean City, Maryland, on the Atlanti ...
) and joined by Sulphur Spring Run where it forms Valley View Island
Valley View Island is an island bar on the South Branch Potomac River near Romney in the U.S. state of West Virginia. The island is formed at the confluence of the South Branch Potomac River with Sulphur Spring Run at the foot of Romney's Yello ...
to the west of town.
Flowing north of Romney, the river still follows the eastern side of Mill Creek Mountain until it creates a horseshoe bend at Wappocomo's Hanging Rocks
Hanging Rocks are perpendicular cliffs rising nearly above the South Branch Potomac River in Hampshire County in the U.S. state of West Virginia. Hanging Rocks are located four miles (6 km) north of Romney at Wappocomo on West Virgini ...
around the George W. Washington plantation, Ridgedale. To the west of Three Churches on the western side of South Branch Mountain
South Branch Mountain is a mountain ridge that runs southwest to northeast through Hampshire and Hardy counties in the Eastern Panhandle of the U.S. state of West Virginia, rising to its greatest elevation of 3,028 feet (923 m) above sea-level in ...
, 3,028 feet (923 m), the South Branch creates a series of bends and flows to the northeast by Springfield through Blue's Ford. After two additional horseshoe bends (meanders), the South Branch flows under the old Baltimore and Ohio Railroad mainline between Green Spring and South Branch Depot, and joins the North Branch to form the Potomac.
Upper Potomac River
This stretch encompasses the section of the Potomac River from the confluence of its North and South Branches throughOpequon Creek
Opequon Creek is an approximately 35 mile U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map accessed August 15, 2011 tributary stream of the Potomac River. It flows into the Potomac northeast of Ma ...
near Shepherdstown, West Virginia
Shepherdstown is a town in Jefferson County, West Virginia, United States, located in the lower Shenandoah Valley along the Potomac River. Home to Shepherd University, the town's population was 1,734 at the time of the 2010 census.
History 18 ...
. Along the way the following tributaries drain into the Potomac: North Branch Potomac River
The North Branch Potomac River flows from Fairfax Stone in West Virginia to its confluence with the South Branch Potomac River near Green Spring, West Virginia, where it turns into the Potomac River proper.
Course
From the Fairfax Stone, th ...
, South Branch Potomac River
The South Branch Potomac River has its headwaters in northwestern Highland County, Virginia near Hightown along the eastern edge of the Allegheny Front. After a river distance of ,U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolu ...
, Town Creek, Little Cacapon River
The Little Cacapon River is a U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map, accessed August 15, 2011 free-flowing tributary of the Potomac River in the center of Hampshire County, West Virgini ...
, Sideling Hill Creek, Cacapon River
The Cacapon River ( ; meaning Medicine Waters), located in the Appalachian Mountains of West Virginia's Eastern Panhandle region, is an shallow river known for its fishing, boating, wildlife, hunting, and wilderness scenery. As part of the Potoma ...
, Sir Johns Run
Sir Johns Run is an U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map accessed August 15, 2011 tributary stream of the Potomac River in Morgan County, West Virginia. For most of its course, Sir Joh ...
, Warm Spring Run
Warm Spring Run is an U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map accessed August 15, 2011 non-navigable tributary stream of the Potomac River in Morgan County of West Virginia's Eastern Pa ...
, Tonoloway Creek Tonoloway Creek, also known as Great Tonoloway Creek, is a U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map accessed August 15, 2011 tributary stream of the Potomac River in the U.S. states of Maryl ...
, Fifteenmile Creek, Sleepy Creek
Sleepy Creek is a U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map accessed August 15, 2011 tributary of the Potomac River in the United States, belonging to the Chesapeake Bay's watershed. The s ...
, Cherry Run
Cherry Run is a U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map, accessed August 15, 2011 meandering stream that forms the northern section of the boundary between Morgan and Berkeley counties i ...
, Back Creek, Conococheague Creek
Conococheague Creek, a tributary of the Potomac River, is a free-flowing stream that originates in Pennsylvania and empties into the Potomac River near Williamsport, Maryland. It is in length,U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset h ...
, and Opequon Creek
Opequon Creek is an approximately 35 mile U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map accessed August 15, 2011 tributary stream of the Potomac River. It flows into the Potomac northeast of Ma ...
.
Lower Potomac River
 This section covers the Potomac from just above Harpers Ferry in West Virginia down to Little Falls, Maryland on the border between Maryland and Washington, DC. Along the way the following tributaries drain into the Potomac:
This section covers the Potomac from just above Harpers Ferry in West Virginia down to Little Falls, Maryland on the border between Maryland and Washington, DC. Along the way the following tributaries drain into the Potomac: Antietam Creek
Antietam Creek () is a U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map, accessed August 15, 2011 tributary of the Potomac River located in south central Pennsylvania and western Maryland in the ...
, Shenandoah River, Catoctin Creek, Catoctin Creek, Tuscarora Creek, Monocacy River
The Monocacy River () is a free-flowing left tributary to the Potomac River, which empties into the Atlantic Ocean via the Chesapeake Bay. The river is long,U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline data ...
, Little Monocacy River The Little Monocacy River is a U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map, accessed August 15, 2011 tributary stream of the Potomac River. Despite its name, the stream does not feed into the Mo ...
, Broad Run, Goose Creek, Broad Run, Horsepen Branch, Little Seneca Creek
Little Seneca Creek is an U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map, accessed August 15, 2011 stream in Montgomery County, Maryland, roughly northwest of Washington, D.C.
Geography
The ...
, Tenmile Creek, Great Seneca Creek
Seneca Creek is a U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map accessed August 15, 2011 stream in Montgomery County, Maryland, USA, roughly northwest of Washington, D.C. It drains into t ...
, Old Sugarland Run, Muddy Branch
Muddy Branch is a tributary stream of the Potomac River in Montgomery County, Maryland, United States, located about northwest of Washington, D.C.
Course
The headwaters of the stream originate in Gaithersburg, and the stream flows southwest f ...
, Nichols Run, Watts Branch, Limekiln Branch, Carroll Branch, Pond Run, Clarks Branch, Mine Run Branch, Difficult Run
Difficult Run is a U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map , accessed August 15, 2011 tributary stream of the Potomac River in Northern Virginia in the United States. The area has had many ...
, Bullneck Run, Rock Run, Scott Run, Dead Run, Turkey Run, Cabin John Creek
Cabin John Creek is a tributary stream of the Potomac River in Montgomery County, Maryland. The watershed covers an area of . The headwaters of the creek originate in the city of Rockville, and the creek flows southward for U.S. Geological Surve ...
, Minnehaha Branch, and Little Falls Branch.
Tidal Potomac River
The Tidal Potomac River lies below theFall Line
A fall line (or fall zone) is the area where an upland region and a coastal plain meet and is typically prominent where rivers cross it, with resulting rapids or waterfalls. The uplands are relatively hard crystalline basement rock, and the coa ...
. This 108-mile (174-km) stretch encompasses the Potomac from a short distance below the Washington, DC
)
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = Clockwise from top left: the Washington Monument and Lincoln Memorial on the National Mall, United States Capitol, Logan Circle, Jefferson Memorial, White House, Adams Morgan ...
- Montgomery County line, just downstream of the Little Falls of the Potomac River
Little Falls is an area of rapids located where the Potomac River crosses the Atlantic Seaboard fall line where Washington, DC, Maryland and Virginia meet. Descending from the harder and older rocks of the Piedmont Plateau to the softer sediment ...
, to the Chesapeake Bay
The Chesapeake Bay ( ) is the largest estuary in the United States. The Bay is located in the Mid-Atlantic region and is primarily separated from the Atlantic Ocean by the Delmarva Peninsula (including the parts: the Eastern Shore of Maryland / ...
.
Along the way the following tributaries drain into the Potomac: Pimmit Run
Pimmit Run is a U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map accessed August 15, 2011 stream in northern Virginia that runs from Fairfax County to the Potomac River at Chain Bridge in the Arli ...
, Gulf Branch
Gulf Branch is a stream in Arlington County, Virginia. From its source southwest of the Gulf Branch Nature Center, Gulf Branch flows on a northeastern course and empties into the Potomac River within the Federal parklands of the George Washington ...
, Donaldson Run
Donaldson Run is a stream in Arlington County, Virginia, Arlington County, Virginia. From its source near Marymount University, Donaldson Run flows on a northeastern course and empties into the Potomac River within the federal parklands of the Ge ...
, Windy Run
Windy Run is a small stream in Arlington County, Virginia. From its source near Lorcom Lane, Windy Run flows on a northeastern course and empties into the Potomac River within the Federal parklands of the George Washington Memorial Parkway.Coordin ...
, Spout Run, Maddox Branch
Maddox Branch is a tributary stream of the Potomac River in Washington, D.C., USA. The historic headwaters of the stream originate in the Tenleytown area in Northwest Washington. The stream flows from the campus of American University south about ...
, Foundry Branch
Foundry Branch is a tributary stream of the Potomac River in Washington, DC. The historic headwaters of the stream originate in the
Tenleytown area in Northwest Washington, however at present the section of the stream north of Massachusetts Aven ...
, Rock Creek, Rocky Run, Tiber Creek
Tiber Creek or Tyber Creek, originally named Goose Creek, is a tributary of the Potomac River in Washington, D.C. It was a free-flowing creek until 1815, when it was channeled to become part of the Washington City Canal. Presently, it flows un ...
, Roaches Run, Washington Channel
The Washington Channel is a channel that parallels the Potomac River in Washington, D.C. It is located between the Southwest Waterfront on the east side and East Potomac Park on the west side. The channel is long, receives outflow from the T ...
, Anacostia River
The Anacostia River is a river in the Mid Atlantic region of the United States. It flows from Prince George's County in Maryland into Washington, D.C., where it joins with the Washington Channel to empty into the Potomac River at Buzzard Point. ...
, Four Mile Run
Four Mile Run is a U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map, accessed August 15, 2011 stream in Northern Virginia that starts near Interstate 66, at Gordon Avenue in Fairfax County and pro ...
, Oxon Creek
Oxon Creek is a stream on the Potomac River which feeds a cove that straddles the border between Washington, D.C. and Prince George's County, Maryland just north of Interstate 495 (Capital Beltway) at Woodrow Wilson Bridge. Oxon Creek heads at the ...
, Hunting Creek
Hunting Creek is a cove and tributary stream of the Potomac River between the City of Alexandria and Fairfax County
Fairfax County, officially the County of Fairfax, is a County (United States), county in the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commo ...
, Broad Creek, Henson Creek, Swan Creek, Piscataway Creek
Piscataway Creek is an U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map, accessed August 15, 2011 tributary of the Potomac River in Prince George's County, Maryland, Prince George's County, Marylan ...
, Little Hunting Creek
Little Hunting Creek is a U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map, accessed August 15, 2011 primarily tidal tributary of the Potomac River located in Fairfax County, Virginia, not to be c ...
, Dogue Creek
Dogue Creek is an U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map , accessed August 15, 2011 tributary of the Potomac River in Fairfax County, Virginia, named for the Tauxenent Indigenous Native ...
, Accotink Creek
Accotink Creek is a U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map, accessed August 15, 2011 tributary stream of the Potomac River in Fairfax County, Virginia, in the United States. At Springfie ...
, Pohick Creek
Pohick Creek is a U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map accessed August 15, 2011 tributary stream of the Potomac River in Fairfax County in the U.S. state of Virginia. It takes its nam ...
, Pomonkey Creek
Pomonkey Creek is a U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map accessed August 15, 2011 tidal tributary of the Potomac River
The Potomac River () drains the Mid-Atlantic United States, ...
, Occoquan River
The Occoquan River is a tributary of the Potomac River in Northern Virginia, where it serves as part of the boundary between Fairfax and Prince William counties.
The river is a scenic area, and several local high schools and colleges use the r ...
, Neabsco Creek
Neabsco Creek is a U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map accessed August 15, 2011 tributary of the lower tidal segment of the Potomac River in eastern Prince William County, Virginia. T ...
, Powell's Creek
Powell's Creek is a tributary of the James River on the south side of the James River in Prince George County, Virginia, United States. The creek borders James River National Wildlife Refuge near Garysville, Virginia. History
In 1730, a tob ...
, Mattawoman Creek
Mattawoman Creek is a U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map, accessed August 15, 2011 coastal-plain tributary to the tidal Potomac River with a mouth at Indian Head, Maryland, downstr ...
, Chicamuxen Creek, Quantico Creek
Quantico Creek is a U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map accessed August 15, 2011 partially tidal tributary of the Potomac River in eastern Prince William County, Virginia. Quantico C ...
, Little Creek, Chopawamsic Creek, Tank Creek
A tank is an armoured fighting vehicle intended as a primary offensive weapon in front-line ground combat. Tank designs are a balance of heavy firepower, strong armour, and good battlefield mobility provided by tracks and a powerful engi ...
, Aquia Creek, Potomac Creek
Potomac Creek is a U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map accessed August 15, 2011 tidal tributary of the Potomac River in King George and Stafford counties, Virginia. Potomac Creek's so ...
, Nanjemoy Creek
Nanjemoy Creek is a , Creek (tidal), tidal tributary of the Potomac River in Charles County, Maryland, Charles County, Maryland, United States, located between Cedar Point Neck and Tayloe Neck. Its watershed area (excluding water) is , with 2% imp ...
, Chotank Creek
King George County is a county (United States), county located in the Commonwealth of Virginia. As of the 2020 United States Census, 2020 census, the population sits at 26,723. Its county seat is the town of King George, Virginia, King George.
...
, Port Tobacco River
The Port Tobacco River is a tidal tributary of the Potomac River located in Charles County, Maryland in the United States. The river is approximately in length.U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe ...
, Popes Creek, Gambo Creek
Gambo may refer to:
Places
* Gambo, Central African Republic, a town in the Central African Republic
* Gambo, Newfoundland and Labrador, a town in northeastern Newfoundland, Newfoundland and Labrador, Canada
Ships
* USS ''West Gambo'' (ID-3220 ...
, Clifton Creek
Clifton Creek is a suburbs and localities (Australia), locality in the Shire of East Gippsland, Victoria (Australia), Victoria, Australia. In the 2016 Australian census, 2016 census, Clifton Creek had a population of 237 people.
Clifton Creek Pr ...
, Piccowaxen Creek, Upper Machodoc Creek
Upper may refer to:
* Shoe upper or ''vamp'', the part of a shoe on the top of the foot
* Stimulant, drugs which induce temporary improvements in either mental or physical function or both
* ''Upper'', the original film title for the 2013 found fo ...
, Wicomico River, Cobb Island
Cobb Island is a small island located at the confluence of the Potomac and Wicomico rivers in southern Charles County, Maryland, United States. It is located approximately south of Washington, and is considered to be within the Washington, D.C ...
, Monroe Creek, Mattox Creek
Mattox Creek is a tributary of the Potomac River in the Washington District of Westmoreland County, Virginia, near the colonial stagecoach stop of Oak Grove. The creek is long,U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution ...
, Popes Creek, Breton Bay, Leonardtown
Breton most often refers to:
*anything associated with Brittany, and generally
**Breton people
**Breton language, a Southwestern Brittonic Celtic language of the Indo-European language family, spoken in Brittany
**Breton (horse), a breed
** Gale ...
, St. Marys River, Yeocomico River
The Yeocomico River is a tidal tributary of the southern portion of the Potomac River in Virginia's Northern Neck. The Yeocomico forms the boundary between Westmoreland and Northumberland counties. Yeocomico is a Native American name roughly t ...
, Coan River
The Coan River is a river in Virginia's Northern Neck region. It is a tributary of the Potomac River
The Potomac River () drains the Mid-Atlantic United States, flowing from the Potomac Highlands into Chesapeake Bay. It is long,U.S. Geolo ...
, and Hull Creek.
History
Natural history
The river itself is at least 3.5 million years old, likely extending back ten to twenty million years before the present when the Atlantic Ocean lowered and exposed coastal sediments along the fall line. This included the area at Great Falls, which eroded into its present form during recent glaciation periods. Thestream gradient Stream gradient (or stream slope) is the grade (slope), grade (or slope) of a stream measured by the ratio of drop in elevation per unit horizontal distance, usually expressed as metre, meters per kilometre, kilometer or Foot (length), feet per mile ...
of the entire river is 0.14%, a drop of 930 m over 652 km.
Human history
 "Potomac" is a European spelling of ''
"Potomac" is a European spelling of ''Patawomeck
Patawomeck is a Native American tribe based in Stafford County, Virginia, along the Potomac River. ''Patawomeck'' is another spelling of Potomac.
The Patawomeck Indian Tribe of Virginia is a state-recognized tribe in Virginia that identifies ...
'', the Algonquian name of a Native American village on its southern bank. Native Americans had different names for different parts of the river, calling the river above Great Falls
Great may refer to: Descriptions or measurements
* Great, a relative measurement in physical space, see Size
* Greatness, being divine, majestic, superior, majestic, or transcendent
People
* List of people known as "the Great"
*Artel Great (born ...
''Cohongarooton'', meaning "honking geese" and "Patawomke" below the Falls, meaning "river of swans". In 1608, Captain John Smith explored the river now known as the Potomac and made drawings of his observations which were later compiled into a map and published in London in 1612. This detail from that map shows his rendition of the river that the local tribes had told him was called the "Patawomeck". The spelling of the name has taken many forms over the years from "Patawomeck
Patawomeck is a Native American tribe based in Stafford County, Virginia, along the Potomac River. ''Patawomeck'' is another spelling of Potomac.
The Patawomeck Indian Tribe of Virginia is a state-recognized tribe in Virginia that identifies ...
" (as on Captain John Smith
John Smith (baptized 6 January 1580 – 21 June 1631) was an English soldier, explorer, colonial governor, Admiral of New England, and author. He played an important role in the establishment of the colony at Jamestown, Virginia, the first pe ...
's map) to "Patomake", "Patowmack", and numerous other variations in the 18th century and now "Potomac". The river's name was officially decided upon as "Potomac" by the Board on Geographic Names
The United States Board on Geographic Names (BGN) is a federal body operating under the United States Secretary of the Interior. The purpose of the board is to establish and maintain uniform usage of geographic names throughout the federal govern ...
in 1931.
 The similarity of the name to the Ancient Greek word for river, ''potamos'', has been noted for more than two centuries but it appears to be due to chance.
The Potomac River brings together a variety of cultures throughout the watershed from the coal miners of upstream West Virginia to the urban residents of the nation's capital and, along the lower Potomac, the watermen of Virginia's Northern Neck.
The similarity of the name to the Ancient Greek word for river, ''potamos'', has been noted for more than two centuries but it appears to be due to chance.
The Potomac River brings together a variety of cultures throughout the watershed from the coal miners of upstream West Virginia to the urban residents of the nation's capital and, along the lower Potomac, the watermen of Virginia's Northern Neck.

 Being situated in an area rich in
Being situated in an area rich in American history
The history of the lands that became the United States began with the arrival of Settlement of the Americas, the first people in the Americas around 15,000 BC. Native American cultures in the United States, Numerous indigenous cultures formed ...
and American heritage has led to the Potomac being nicknamed "the Nation's River". George Washington
George Washington (February 22, 1732, 1799) was an American military officer, statesman, and Founding Father who served as the first president of the United States from 1789 to 1797. Appointed by the Continental Congress as commander of ...
, the first President of the United States
The president of the United States (POTUS) is the head of state and head of government of the United States of America. The president directs the executive branch of the federal government and is the commander-in-chief of the United States ...
, was born in, surveyed, and spent most of his life within, the Potomac basin. All of Washington, D.C., the nation's capital city
A capital city or capital is the municipality holding primary status in a country, state, province, department, or other subnational entity, usually as its seat of the government. A capital is typically a city that physically encompasses t ...
, also lies within the watershed. The 1859 siege of Harper's Ferry
Harpers Ferry is a historic town in Jefferson County, West Virginia. It is located in the lower Shenandoah Valley. The population was 285 at the 2020 census. Situated at the confluence of the Potomac and Shenandoah rivers, where the U.S. stat ...
at the river's confluence with the Shenandoah was a precursor to numerous epic battles of the American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861 – May 26, 1865; also known by other names) was a civil war in the United States. It was fought between the Union ("the North") and the Confederacy ("the South"), the latter formed by states th ...
in and around the Potomac and its tributaries, such as the 1861 Battle of Ball's Bluff
The Battle of Ball's Bluff was an early battle of the American Civil War fought in Loudoun County, Virginia, on October 21, 1861, in which Union Army forces under Major General George B. McClellan suffered a humiliating defeat.
The operation wa ...
and the 1862 Battle of Shepherdstown
The Battle of Shepherdstown, also known as the Battle of Boteler's Ford, took place September 19–20, 1862, at Boteler's Ford along the Potomac River, during the Maryland campaign of the American Civil War. After the Battle of Antietam on S ...
.  General Robert E. Lee crossed the river, thereby invading the North and threatening Washington, D.C., twice in campaigns climaxing in the battles of
General Robert E. Lee crossed the river, thereby invading the North and threatening Washington, D.C., twice in campaigns climaxing in the battles of Antietam
The Battle of Antietam (), or Battle of Sharpsburg particularly in the Southern United States, was a battle of the American Civil War fought on September 17, 1862, between Confederate Gen. Robert E. Lee's Army of Northern Virginia and Union G ...
(September 17, 1862) and Gettysburg (July 1–3, 1863). Confederate General Jubal Early
Jubal Anderson Early (November 3, 1816 – March 2, 1894) was a Virginia lawyer and politician who became a Confederate States of America, Confederate general during the American Civil War. Trained at the United States Military Academy, Early r ...
crossed the river in July 1864 on his attempted raid on the nation's capital. The river not only divided the Union from the Confederacy, but also gave name to the Union's largest army, the Army of the Potomac
The Army of the Potomac was the principal Union Army in the Eastern Theater of the American Civil War. It was created in July 1861 shortly after the First Battle of Bull Run and was disbanded in June 1865 following the surrender of the Confede ...
.
The Patowmack Canal
The Patowmack Canal, sometimes called the Potomac Canal, is a series of five inoperative canals located in Maryland and Virginia, United States, that was designed to bypass rapids in the Potomac River upstream of the present Washington, D.C., ...
was intended by George Washington to connect the Tidewater region
Tidewater refers to the north Atlantic coastal plain region of the United States of America.
Definition
Culturally, the Tidewater region usually includes the low-lying plains of southeast Virginia, northeastern North Carolina, southern Mary ...
near Georgetown with Cumberland, Maryland. Started in 1785 on the Virginia side of the river, it was not completed until 1802. Financial troubles led to the closure of the canal
Canals or artificial waterways are waterways or engineered channels built for drainage management (e.g. flood control and irrigation) or for conveyancing water transport vehicles (e.g. water taxi). They carry free, calm surface flow un ...
in 1830. The Chesapeake and Ohio Canal
The Chesapeake and Ohio Canal, abbreviated as the C&O Canal and occasionally called the "Grand Old Ditch," operated from 1831 until 1924 along the Potomac River between Washington, D.C. and Cumberland, Maryland. It replaced the Potomac Canal, ...
operated along the banks of the Potomac in Maryland from 1831 to 1924 and also connected Cumberland to Washington, D.C. This allowed freight to be transported around the rapids known as the Great Falls of the Potomac River
Great Falls is a series of rapids and waterfalls on the Potomac River, upstream from Washington, D.C., on the border of Montgomery County, Maryland and Fairfax County, Virginia. Great Falls Park, managed as part of George Washington Memorial ...
, as well as many other, smaller rapids.
Washington, D.C. began using the Potomac as its principal source of drinking water
Drinking water is water that is used in drink or food preparation; potable water is water that is safe to be used as drinking water. The amount of drinking water required to maintain good health varies, and depends on physical activity level, a ...
with the opening of the Washington Aqueduct
The Washington Aqueduct is an aqueduct that provides the public water supply system serving Washington, D.C., and parts of its suburbs, using water from the Potomac River. One of the first major aqueduct projects in the United States, the Aquedu ...
in 1864, using a water intake
A water supply network or water supply system is a system of engineered hydrologic and hydraulic components that provide water supply. A water supply system typically includes the following:
# A drainage basin (see water purification – source ...
constructed at Great Falls.Ways, Harry C. (1996). ''The Washington Aqueduct: 1852-1992.'' (Baltimore, MD: U.S. Army Corps of Engineers, Baltimore District)
Hydrology
Water supply and water quality
An average of approximately of water is withdrawn daily from the Potomac in the Washington area forwater supply
Water supply is the provision of water by public utilities, commercial organisations, community endeavors or by individuals, usually via a system of pumps and pipes. Public water supply systems are crucial to properly functioning societies. Thes ...
, providing about 78 percent of the region's total water usage, this amount includes approximately 80 percent of the drinking water consumed by the region's estimated 6.1 million residents.
 As a result of damaging floods in 1936 and 1937, the Army Corps of Engineers proposed the
As a result of damaging floods in 1936 and 1937, the Army Corps of Engineers proposed the Potomac River basin reservoir projects The Potomac River basin reservoir projects were U.S. Army Corps of Engineers programs that sought to regulate the flow of the Potomac River to control flooding, to assure a reliable water supply for Washington, D.C., and to provide recreational oppo ...
, a series of dams that were intended to regulate the river and to provide a more reliable water supply. One dam was to be built at Little Falls, just north of Washington, backing its pool up to Great Falls. Just above Great Falls, the much larger Seneca Dam
Seneca Dam was the last in a series of dams proposed on the Potomac River in the area of the Great Falls of the Potomac. Apart from small-scale dams intended to divert water for municipal use in the District of Columbia and into the Chesapeake an ...
was proposed whose reservoir would extend to Harpers Ferry. Several other dams were proposed for the Potomac and its tributaries.
When detailed studies were issued by the Corps in the 1950s, they met sustained opposition, led by U.S. Supreme Court
The Supreme Court of the United States (SCOTUS) is the highest court in the federal judiciary of the United States. It has ultimate appellate jurisdiction over all U.S. federal court cases, and over state court cases that involve a point o ...
Justice William O. Douglas
William Orville Douglas (October 16, 1898January 19, 1980) was an American jurist who served as an associate justice of the Supreme Court of the United States, who was known for his strong progressive and civil libertarian views, and is often ci ...
, resulting in the plans' abandonment. The only dam project that did get built was Jennings Randolph Lake
Jennings Randolph Lake is a reservoir of located on the North Branch Potomac River in Garrett County, Maryland and Mineral County, West Virginia. It is approximately eight miles upstream of Bloomington, Maryland, and approximately five miles n ...
on the North Branch.
The Corps built a supplementary water intake for the Washington Aqueduct at Little Falls in 1959.Scott, Pamela (2007)"Capital Engineers: The U.S. Army Corps of Engineers in the Development of Washington, D.C., 1790–2004."
(Washington, DC: U.S. Army Corps of Engineers.) Publication No. EP 870-1-67. p. 256. In 1940
Congress
A congress is a formal meeting of the representatives of different countries, constituent states, organizations, trade unions, political parties, or other groups. The term originated in Late Middle English to denote an encounter (meeting of ...
passed a law authorizing the creation of an interstate compact
The Dwight D. Eisenhower National System of Interstate and Defense Highways, commonly known as the Interstate Highway System, is a network of controlled-access highways that forms part of the National Highway System in the United States. Th ...
to coordinate water quality management among states in the Potomac basin. Maryland, West Virginia, Pennsylvania, Virginia, and the District of Columbia agreed to establish the Interstate Commission on the Potomac River Basin
The 'Interstate Commission on the Potomac River Basin(ICPRB) is an agency composed of commissioners representing the federal government, the states of Maryland, Pennsylvania, Virginia, West Virginia, and the District of Columbia. The ICPRB mission ...
. The compact was amended in 1970 to include coordination of water supply issues and land use issues related to water quality.ICPRB"Potomac Timeline."
Updated 2008-04-15.
mining
Mining is the extraction of valuable minerals or other geological materials from the Earth, usually from an ore body, lode, vein, seam, reef, or placer deposit. The exploitation of these deposits for raw material is based on the economic ...
and agriculture
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled people to ...
upstream and urban sewage and runoff
Runoff, run-off or RUNOFF may refer to:
* RUNOFF, the first computer text-formatting program
* Runoff or run-off, another name for bleed, printing that lies beyond the edges to which a printed sheet is trimmed
* Runoff or run-off, a stock marke ...
downstream, the water quality
Water quality refers to the chemical, physical, and biological characteristics of water based on the standards of its usage. It is most frequently used by reference to a set of standards against which compliance, generally achieved through tr ...
of the Potomac River deteriorated. This created conditions of severe eutrophication
Eutrophication is the process by which an entire body of water, or parts of it, becomes progressively enriched with minerals and nutrients, particularly nitrogen and phosphorus. It has also been defined as "nutrient-induced increase in phytopla ...
. It is said that President Abraham Lincoln
Abraham Lincoln ( ; February 12, 1809 – April 15, 1865) was an American lawyer, politician, and statesman who served as the 16th president of the United States from 1861 until his assassination in 1865. Lincoln led the nation thro ...
used to escape to the highlands on summer nights to escape the river's stench. In the 1960s, with dense green algal
Algae (; singular alga ) is an informal term for a large and diverse group of photosynthetic eukaryotic organisms. It is a polyphyletic grouping that includes species from multiple distinct clades. Included organisms range from unicellular mi ...
blooms covering the river's surface, President Lyndon Johnson declared the river "a national disgrace" and set in motion a long-term effort to reduce pollution
Pollution is the introduction of contaminants into the natural environment that cause adverse change. Pollution can take the form of any substance (solid, liquid, or gas) or energy (such as radioactivity, heat, sound, or light). Pollutants, the ...
from sewage and restore the beauty and ecology of this historic river. One of the significant pollution control projects at the time was the expansion of the Blue Plains Advanced Wastewater Treatment Plant
Blue Plains Advanced Wastewater Treatment Plant, located at 5000 Overlook Ave SW, Washington, DC 20032, is the largest advanced wastewater treatment plant in the world. The facility is operated by the District of Columbia Water and Sewer Author ...
, which serves Washington and several surrounding communities. Enactment of the 1972 Clean Water Act led to construction or expansion of additional sewage treatment
Sewage treatment (or domestic wastewater treatment, municipal wastewater treatment) is a type of wastewater treatment which aims to remove contaminants from sewage to produce an effluent that is suitable for discharge to the surrounding e ...
plants in the Potomac watershed. Controls on phosphorus
Phosphorus is a chemical element with the symbol P and atomic number 15. Elemental phosphorus exists in two major forms, white phosphorus and red phosphorus, but because it is highly reactive, phosphorus is never found as a free element on Ear ...
, one of the principal contributors to eutrophication, were implemented in the 1980s, through sewage plant upgrades and restrictions on phosphorus in detergents.
By the end of the 20th century, notable success had been achieved, as massive algal blooms vanished and recreational fishing and boating rebounded. Still, the aquatic habitat
In ecology, the term habitat summarises the array of resources, physical and biotic factors that are present in an area, such as to support the survival and reproduction of a particular species. A species habitat can be seen as the physical ...
of the Potomac River and its tributaries remain vulnerable to eutrophication, heavy metals, pesticides and other toxic chemicals, over-fishing, alien species
An introduced species, alien species, exotic species, adventive species, immigrant species, foreign species, non-indigenous species, or non-native species is a species living outside its native distributional range, but which has arrived there ...
, and pathogen
In biology, a pathogen ( el, πάθος, "suffering", "passion" and , "producer of") in the oldest and broadest sense, is any organism or agent that can produce disease. A pathogen may also be referred to as an infectious agent, or simply a germ ...
s associated with fecal coliform
A fecal coliform (British: faecal coliform) is a facultatively anaerobic, rod-shaped, gram-negative, non-sporulating bacterium. Coliform bacteria generally originate in the intestines of warm-blooded animals. Fecal coliforms are capable of growth ...
bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among ...
and shellfish diseases. In 2005 two federal agencies, the US Geological Survey
The United States Geological Survey (USGS), formerly simply known as the Geological Survey, is a scientific agency of the United States government. The scientists of the USGS study the landscape of the United States, its natural resources, and ...
and the Fish and Wildlife Service
The United States Fish and Wildlife Service (USFWS or FWS) is an agency within the United States Department of the Interior dedicated to the management of fish, wildlife, and natural habitats. The mission of the agency is "working with othe ...
, began to identify fish in the Potomac and tributaries that exhibited "intersex" characteristics, as a result of endocrine disruption
Endocrine disruptors, sometimes also referred to as hormonally active agents, endocrine disrupting chemicals, or endocrine disrupting compounds are chemicals that can interfere with endocrine (or hormonal) systems. These disruptions can cause ca ...
caused by some form of pollution.
On November 13, 2007, the Potomac Conservancy, an environmental group, issued the river a grade of "D-plus", citing high levels of pollution and the reports of "intersex
Intersex people are individuals born with any of several sex characteristics including chromosome patterns, gonads, or genitals that, according to the Office of the United Nations High Commissioner for Human Rights, "do not fit typical bin ...
" fish. Since then, the river has improved with a reduction in nutrient runoff, return of fish populations, and land protection along the river. As a result, the same group issued a grade of "B" for 2017 and 2018. In March 2019, the Potomac Riverkeeper Network launched a laboratory boat dubbed the "Sea Dog", which will be monitoring water quality in the Potomac and providing reports to the public on a weekly basis; in that same month, the catching near Fletcher's Boat House of a Striped Bass estimated to weigh 35 lbs was seen as a further indicator of the continuing improvement in the health of the river.
Discharge
 The average daily flow during the
The average daily flow during the water year
A water year (also called ''hydrological year'', ''discharge year'' or ''flow year'') is a term commonly used in hydrology to describe a time period of 12 months for which precipitation totals are measured. Its beginning differs from the calendar ...
s 1931–2018 was /s. The highest average daily flow ever recorded on the Potomac at Little Falls, Maryland (near Washington, D.C.), was in March 1936 when it reached /s. The lowest average daily flow ever recorded at the same location was /s in September 1966 The highest crest of the Potomac ever registered at Little Falls was 28.10 ft, on March 19, 1936;
however, the most damaging flood to affect Washington, DC and its metropolitan area was that of October 1942.
Legal issues
For 400 years Maryland and Virginia have disputed control of the Potomac and its North Branch since both states' originalcolonial charter A charter is a document that gives colonies the legal rights to exist. Charters can bestow certain rights on a town, city, university, or other institution.
Colonial charters were approved when the king gave a grant of exclusive powers for the go ...
s grant the entire river rather than half of it as is normally the case with boundary rivers. In its first state constitution
A constitution is the aggregate of fundamental principles or established precedents that constitute the legal basis of a polity, organisation or other type of entity and commonly determine how that entity is to be governed.
When these princ ...
adopted in 1776, Virginia ceded its claim to the entire river but reserved free use of it, an act disputed by Maryland. Both states acceded to the 1785 Mount Vernon Compact and the 1877 Black-Jenkins Award which granted Maryland the river bank-to-bank from the low-water mark on the Virginia side while permitting Virginia full riparian rights
Riparian water rights (or simply riparian rights) is a system for allocating water among those who possess land along its path. It has its origins in English common law. Riparian water rights exist in many jurisdictions with a common law heri ...
short of obstructing navigation.
From 1957 to 1996, the Maryland Department of the Environment
The Maryland Department of the Environment (MDE) is a government agency in the state of Maryland that implements and enforces environmental protection laws and programs. The agency's stated vision is "Healthy, vibrant and sustainable communities a ...
(MDE) routinely issued permits applied for by Virginia entities concerning the use of the Potomac. However, in 1996 the MDE denied a permit submitted by the Fairfax County Water Authority Fairfax County Water Authority (FCWA or more recently Fairfax Water for short) is the main water company in the Northern Virginia region of the United States, and one of the four major water providers in the Washington, D.C. metropolitan area (the ...
to build a water intake 725 feet (220 m) offshore, citing potential harm to Maryland's interests by an increase in Virginia sprawl caused by the project. After years of failed appeals within the Maryland government's appeal processes, in 2000 Virginia took the case to the Supreme Court of the United States, which exercises original jurisdiction in cases between two states. Maryland claimed Virginia lost its riparian rights by acquiescing to MDE's permit process for 63 years (MDE began its permit process in 1933). A Special Master
In the law of the United States, a special master is generally a subordinate official appointed by a judge to ensure judicial orders are followed, or in the alternative, to hear evidence on behalf of the judge and make recommendations to the jud ...
appointed by the Supreme Court to investigate recommended the case be settled in favor of Virginia, citing the language in the 1785 Compact and the 1877 Award. On December 9, 2003, the Court agreed in a 7–2 decision.
 The original charters are silent as to which branch from the upper Potomac serves as the boundary, but this was settled by the 1785 Compact. When West Virginia
The original charters are silent as to which branch from the upper Potomac serves as the boundary, but this was settled by the 1785 Compact. When West Virginia seceded
Secession is the withdrawal of a group from a larger entity, especially a political entity, but also from any organization, union or military alliance. Some of the most famous and significant secessions have been: the former Soviet republics lea ...
from Virginia in 1863, the question of West Virginia's succession in title to the lands between the branches of the river was raised, as well as title to the river itself. Claims by Maryland to West Virginia land north of the South Branch (all of Mineral
In geology and mineralogy, a mineral or mineral species is, broadly speaking, a solid chemical compound with a fairly well-defined chemical composition and a specific crystal structure that occurs naturally in pure form.John P. Rafferty, ed. (2 ...
and Grant
Grant or Grants may refer to:
Places
*Grant County (disambiguation)
Australia
* Grant, Queensland, a locality in the Barcaldine Region, Queensland, Australia
United Kingdom
* Castle Grant
United States
* Grant, Alabama
* Grant, Inyo County, ...
Counties and parts of Hampshire
Hampshire (, ; abbreviated to Hants) is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan county in western South East England on the coast of the English Channel. Home to two major English cities on its south coast, Southampton and Portsmouth, Hampshire ...
, Hardy, Tucker
Tucker may refer to:
Places United States
* Tucker, Arkansas
* Tucker, Georgia
* Tucker, Mississippi
* Tucker, Missouri
* Tucker, Utah, ghost town
* Tucker County, West Virginia
Outer space
* Tucker (crater), a small lunar impact crater in the s ...
and Pendleton Counties) and by West Virginia to the Potomac's high-water mark were rejected by the Supreme Court in two separate decisions in 1910.
Flora and Fauna
Fish
 A variety of fish inhabit the Potomac, including bass,
A variety of fish inhabit the Potomac, including bass, muskellunge
The muskellunge ''(Esox masquinongy)'', often shortened to muskie, musky or lunge is a species of large freshwater predatory fish native to North America. It is the largest member of the pike family, Esocidae.
Origin of name
The name "muskell ...
, pike
Pike, Pikes or The Pike may refer to:
Fish
* Blue pike or blue walleye, an extinct color morph of the yellow walleye ''Sander vitreus''
* Ctenoluciidae, the "pike characins", some species of which are commonly known as pikes
* ''Esox'', genus of ...
, walleye
The walleye (''Sander vitreus'', synonym ''Stizostedion vitreum''), also called the yellow pike or yellow pickerel, is a freshwater perciform fish native to most of Canada and to the Northern United States. It is a North American close relat ...
. The northern snakehead
The northern snakehead (''Channa argus'') is a species of snakehead fish native to China, Russia, North Korea, and South Korea, ranging from the Amur River to Hainan. It has been introduced to other regions, where it is considered invasive. In ...
, an invasive species resembling the native bowfin, lamprey
Lampreys (sometimes inaccurately called lamprey eels) are an ancient extant lineage of jawless fish of the order Petromyzontiformes , placed in the superclass Cyclostomata. The adult lamprey may be characterized by a toothed, funnel-like s ...
, and American eel, was first seen in 2004. Many types of sunfish are also present in the Potomac and its headwaters. Although rare, bull shark
The bull shark (''Carcharhinus leucas''), also known as the Zambezi shark (informally zambi) in Africa and Lake Nicaragua shark in Nicaragua, is a species of requiem shark commonly found worldwide in warm, shallow waters along coasts and in ri ...
s can be found.
After having been depressed for many decades, the river's population of American Shad is currently re-bounding as a result of the ICPRB
The 'Interstate Commission on the Potomac River Basin(ICPRB) is an agency composed of commissioners representing the federal government, the states of Maryland, Pennsylvania, Virginia, West Virginia, and the District of Columbia. The ICPRB mission ...
's successful "American Shad Restoration Project" that was begun in 1995. In addition to stocking the river with more than 22 million shad fry, the Project supervised the construction of a fishway that was built to facilitate the passage of adults around the Little Falls Dam on the way to their traditional spawning grounds upstream.
Mammals
elk
The elk (''Cervus canadensis''), also known as the wapiti, is one of the largest species within the deer family, Cervidae, and one of the largest terrestrial mammals in its native range of North America and Central and East Asia. The common ...
, wolves (both gray
Grey (more common in British English) or gray (more common in American English) is an intermediate color between black and white. It is a neutral or achromatic color, meaning literally that it is "without color", because it can be composed o ...
and red
Red is the color at the long wavelength end of the visible spectrum of light, next to orange and opposite violet. It has a dominant wavelength of approximately 625–740 nanometres. It is a primary color in the RGB color model and a secondar ...
) and cougars were still present at that time, but had been hunted to extirpation by the middle of the 19th century. Among the denizens of the Potomac's banks, beavers and otters met a similar fate, while small populations of American mink and American martens survived into the 20th century in some secluded areas.
There is no record of early settlers having observed marine mammals in the Potomac, but several sightings of Atlantic bottle-nosed dolphins (''Tursiops truncatus'') were reported during the 19th century. In July 1844. a pod of 14 adults and young was followed up the river by men in boats as high as the Aqueduct Bridge (approximately the same location occupied by Key Bridge today).
Since 2015, perhaps as a result of warmer temperatures, rising water levels in the Chesapeake Bay and improving water quality in the Potomac, unprecedented numbers of Atlantic bottle-nosed dolphins have been observed in the river. According to Dr Janet Mann of Georgetown University'Potomac-Chesapeake Dolphin Project
more than 500 individual members of the species have been identified in the Potomac during this period.
Birds
Reptiles


Amphibians
Additional images
Upper and lower Potomac


Tidal Potomac




Other

See also
*Air Florida Flight 90
Air Florida Flight 90 was a scheduled U.S. domestic passenger flight operated by Air Florida from Washington National Airport (now Ronald Reagan Washington National Airport) to Fort Lauderdale–Hollywood International Airport, with an interme ...
* List of cities and towns along the Potomac River
This is a list of cities, towns, and communities along the Potomac River and its branches in the United States.
Potomac River
Alphabetically
*Alexandria, Virginia
*Arlington, Virginia
*Belle Haven, Fairfax County, Virginia, Belle Haven, Virgi ...
* List of crossings of the Potomac River
This is a list of bridges and other crossings of the Potomac River and its North and South branches. Within each section, crossings are listed from the source moving downstream.
Potomac River
This list contains only crossings of the main channel. ...
* List of islands on the Potomac River
This is a list of islands on the Potomac River and its North and South branches. Because the Potomac belongs to Maryland, the majority of its islands lie within that state with some exceptions including portions located in the District of Columbia ...
* List of rivers of Maryland
List of rivers of Maryland (U.S. state).
The list is arranged by drainage basin from east to west, with respective tributaries indented under each larger stream's name and ordered from downstream to upstream.
By drainage basin
Delaware River
* ...
* List of rivers of Virginia
* List of rivers of West Virginia
This is a list of rivers in the U.S. state of West Virginia.
List of West Virginia rivers includes streams formally designated as rivers. There are also smaller streams (i.e., branches, creeks, drains, forks, licks, runs, etc.) in the state. Ex ...
* List of tributaries of the Potomac River
* List of variant names of the Potomac River
The following have been listed as variant names of the Potomac River throughout its history by the Geographic Names Information System. The Board on Geographic Names
The United States Board on Geographic Names (BGN) is a federal body operating u ...
* Potomac Heritage Trail
The Potomac Heritage Trail, also known as the Potomac Heritage National Scenic Trail or the PHT, is a designated National Scenic Trail corridor spanning parts of the mid-Atlantic region of the United States that will connect various trails and hi ...
Notes and references
Notes
* * * * * *References
Works cited
* Rice, James D., ''Nature and History in the Potomac Country: From Hunter-Gatherers to the Age of Jefferson.'' (2009), Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press; ; * Smith, J. Lawrence, ''The Potomac Naturalist: The Natural History of the Headwaters of the Historic Potomac'' (1968), Parsons, WV: McClain Printing Co.; ;External links
Advanced Hydrologic Prediction Service
Baltimore/Washington (Sterling, VA)
- including Potomac River levels ** Potomac River level a
Williamsport
** Potomac River level a
Harpers Ferry
** Potomac River level a
Point of Rocks
** Potomac River level a
Little Falls
** Potomac River level a
Wisconsin Avenue
''Geology of the National Capital Region: Field Trip Guidebook'' (2004) edited by Scott Southworth, William Chapin Burton, Reston, VA: U.S. Geological Survey
''Guide to Spring Wildflowers on the Towpath'' (2010) compiled by the C&O Canal Association Nature Committee
Interstate Commission on the Potomac River Basin (ICPRB)
Potomac Conservancy
Potomac Heritage National Scenic Trail
Potomac Riverkeeper
Potomac Timeline
(focus on water quality) by ICPRB
Potomac Watershed Partnership
Potomac Watershed Roundtable
Prince William Conservation Alliance
Stewards of the Potomac Highlands
South Branch Consortium
also available in ttps://pubs.usgs.gov/bul/1471/report.pdf downloadable pdf format* [https://pubs.usgs.gov/of/1997/0060/report.pdf ''The Seven-Storey River: Geomorphology of the Potomac River Channel Between Blockhouse Point, Maryland, and Georgetown, District of Columbia, With Emphasis on the Gorge Complex Below Great Falls'' (1997) by E-an Zen, Reston, VA: US Geological Survey]
VEGETATION ECOLOGY OF THE POTOMAC GORGE
by the Virginia Department of Conservation and Recreation, Division of Natural Heritage
West Virginia Division of Natural Resources
West Virginia Rivers Coalition
* ttp://www.switchfisher.com/admin/CatchGuides/CG-UPCatchguide.html Wade and Shoreline Fishing the Potomac River for Smallmouth Bass {{Authority control Rivers of Washington, D.C. Rivers of Maryland Rivers of Virginia Rivers of West Virginia Monongahela National Forest History of West Virginia Borders of Maryland Borders of Virginia Borders of West Virginia American Heritage Rivers Tributaries of the Chesapeake Bay